Part 1: How to query REST data with JDBC applications
Access REST data with your applications
In this four part series, we are going to guide you through using the Autonomous REST Connector to query REST endpoints with a JDBC application. The Progress DataDirect Autonomous REST Connector for JDBC is a driver that provides SQL read and update access to JSON, XML, and CSV REST API data sources. In addition to getting you started in this tutorial, we will cover the following topics in subsequent entries in the series:
- Part 2: How to query data from multiple REST endpoints
- Part 3: How to edit auto-generated schema for REST endpoints
- Part 4: How to configure paging for REST data
The Autonomous REST Connector samples JSON responses from REST APIs and normalizes them to expose them as relational tables. This allows you to use the full capabilities of SQL to access your data, including joining data returned from different endpoints.
To get started with the Autonomous REST Connector, we will walk you through the process of connecting to a REST service from a JDBC SQL tool, Dbeaver. This tutorial will give you an overview of how flexible the Autonomous REST Connector is and how it works.
For the purposes of demonstration, we will use the REST API for Yelp as our data source for this tutorial. Yelp is a popular website that provides reviews for restaurants and businesses. By querying the Yelp REST API, you can retrieve data and reviews about restaurants and businesses featured on the site.
This tutorial covers the following:
About the Yelp API
To use the Yelp Fusion API, you must first obtain a client ID and API key. To do so, you need to register as a developer and create an app on the Yelp developer site. Note that you must provide the following information when creating your app:
- App name
- Industry
- Contact email
- Description
After you create your app, you will be provided with the Client ID and API Key that are used to authenticate to the Yelp Fusion API.
There are a number of endpoints that comprise the YELP API; however, to get started, we will use the Category endpoint:
https://api.yelp.com/v3/categories
The Category endpoint returns all the business categories used in Yelp. To retrieve the response from this endpoint, you can send a GET request to the endpoint URI with an Authentication header containing your API key. Next, you can query the Category endpoint using the Autonomous REST Connector for JDBC and your JDBC application.
Download and install the Autonomous REST Connector for JDBC on Windows
- Click the Try Now button.
The Autonomous REST Connector for JDBC provides JDBC connectivity to Yelp and many other REST APIs.
- When prompted, provide your details, such as name and email address; then, click DOWNLOAD.
- Extract the contents of the installer zip file into a temporary directory; then, double-click the installer program:
PROGRESS_DATADIRECT_JDBC_INSTALL.exe - Follow the prompts to complete the installation.
Configure an analytics or SQL tool to use the connector
You must configure your analytics or SQL tool to use the connector before you can query REST data. In this section, we will use Dbeaver, a SQL query tool, to demonstrate the configuration process. However, this process will vary depending on the tool you are using.
Note: You can also use the SQL Editor tool in the Autonomous REST Composer interface to test your queries. Because the SQL Editor is embedded with the Autonomous REST Connector, it does not require you to register the connector.
To configure Dbeaver to use the connector:
- Open Dbeaver.
- Click Database > Driver Manager. The Driver Manager dialog opens.
- Click New.
- In the Create new driver dialog, provide values for the following fields:
- Driver Name: Enter the name you would like to call your driver. For example,
Autonomous REST Connector. - Class Name:
com.ddtek.jdbc.autorest.AutoRESTDriver
- Driver Name: Enter the name you would like to call your driver. For example,
- Select the Libraries tab; then, click Add file.
- Navigate to the location of the
autorest.jarfile; then, click OK. The default location of the connector jar file is:C:\Program Files\Progress\DataDirect\JDBC\lib\60\autorest.jarThe form should have the information as shown below, when finished with the steps above.
- Click OK to register the connector.
Sample and Query the Yelp API
After configuring your analytics or SQL tool, you are ready to sample and query Yelp data. The connector samples data from the endpoint at connection. During sampling, the connector queries the Yelp endpoint, normalizes the JSON data, and maps it to a tabular view. After the data is mapped to a tabular view, you can begin executing SQL queries against the data.
The following procedure shows us how to use the Autonomous REST Connector to sample Yelp data and query it with Dbeaver.
- From Dbeaver, select Database > New Database Connection.
- Select the name of your driver (Autonomous REST Connector in this example). Then, click Next.
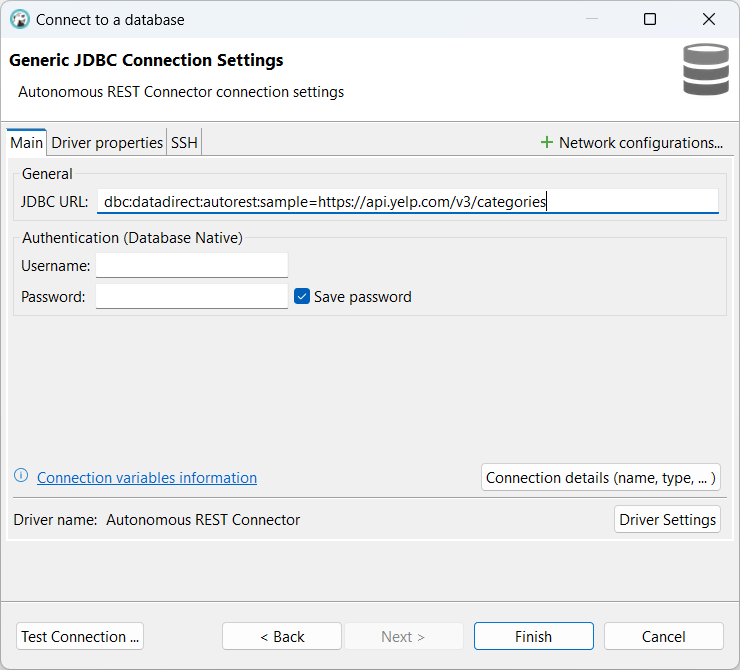
- Enter the JDBC URL. The Sample connection property is used to specify the endpoint you want the connector to query. In this example, the Yelp Categories endpoint is being sampled.
jdbc:datadirect:autorest:sample=https://api.yelp.com/v3/categories - Select the Driver properties tab and enter the required authentication information. For Yelp, the following must be provided:
- AuthenticationMethod:
BearerToken - SecurityToken: Enter your Yelp API Key.
- AuthenticationMethod:
- Click Test Connection to connect. Then, click OK.
- Open a new SQL editor in Dbeaver by going to SQL Editor > New SQL Script. Then select the connection we just created.
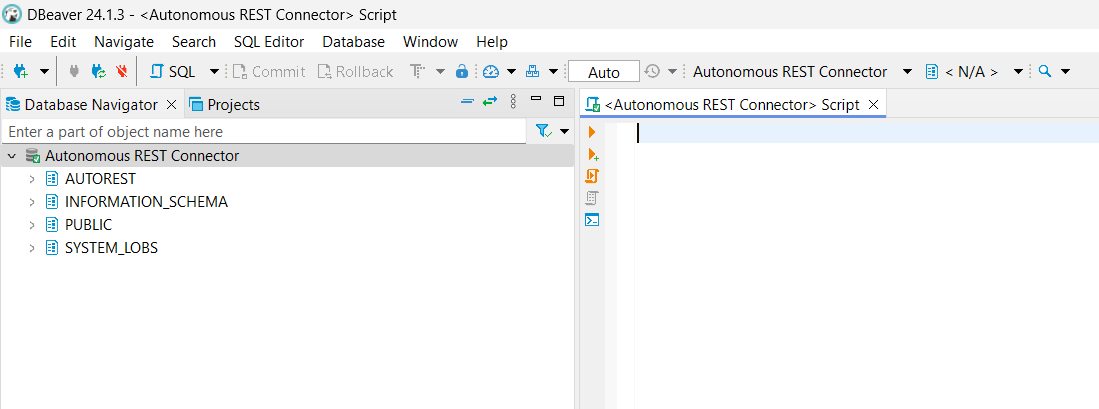
- To view the sampled categories data, expand the AUTOREST schema in the Database Navigator pane. The connector has normalized the JSON data it obtained from the categories endpoint and exposed it into relational tables, such as
COUNTRY_BLACKLISTandPARENT_ALIASES. - In the SQL Editor pane, run queries against the tables exposed by the categories endpoint. Here are sample queries you can try:
SELECT * FROM V3_CATEGORIESSELECT * FROM V3_CATEGORIES WHERE alias LIKE '%food%'SELECT C.ALIAS, C.TITLE, PA.PARENT_ALIASE, PA.POSITION FROM V3_CATEGORIES C INNER JOIN PARENT_ALIASES PA ON PA.V3_CATEGORIES_ALIAS = C.ALIASSELECT C.ALIAS, C.TITLE, CB.COUNTRY_BLACKLIST, CB.POSITION FROM V3_CATEGORIES C INNER JOIN COUNTRY_BLACKLIST CB ON CB.V3_CATEGORIES_ALIAS = C.ALIASSELECT C.ALIAS, C.TITLE, CW.COUNTRY_WHITELIST, CW.POSITION FROM V3_CATEGORIES C INNER JOIN COUNTRY_WHITELIST CW ON CW.V3_CATEGORIES_ALIAS = C.ALIAS
You may have noticed that several of the example queries use the ALIAS field from V3_CATEGORIES table when querying other tables. This is because the ALIAS field was determined to be the primary key by the driver. When sampling, the driver determines which field in the parent table, V3_CATEGORIES in this example, is best suited to be the primary key. Child tables, such as COUNTRY_BLACKLIST and COUNTRY_WHITELIST, use this field, along with the POSITION field, to form the foreign key relationship between tables. Note that you can determine the primary key by querying the _CONFIGURATION table. For example, you receive the following schema for the Categories endpoint:.
{ "v3_categories": {
"#path": [
"https://api.yelp.com/v3/categories /categories"
],
"alias": "VarChar(48), #key",
"title": "VarChar(52)," "parent_aliases[]": "VarChar(34)",
"country_whitelist[]": "VarChar(3)",
"country_blacklist[]": "VarChar(3)"
}
}The field designated as the primary key is indicated by the #key element. In this example, the primary key is the alias field.
What's next
In this tutorial, we sampled and queried a single REST endpoint using SQL, but that is just the beginning. In the next section, we will demonstrate how to query from multiple endpoints. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or issues.
Contact us if you have questions about Progress DataDirect for JDBC drivers or any Progress products.
More information
The Autonomous REST Connector provides JDBC and ODBC connectivity to Yelp, GitHub, Jira, and many other REST APIs.